What to remember:
- Hyperpermeability is also called “Leaky gut syndrome”, literally leaky gut syndrome, or “permeable gut”.
- This is a condition where the protective barrier of our intestine becomes more permeable than normal, causing unwanted substances to pass into our bloodstream.
- The causes of intestinal hyperpermeability are numerous and involve a large number of mechanisms.
- Leaky gut can go unnoticed because it's difficult to feel directly. Associated symptoms can also be attributed to other conditions, making diagnosis more complex.
- Digestive problems, immune system disorders or even chronic fatigue are symptoms that can lead to intestinal porosity.
- A balanced diet or certain food supplements can help combat intestinal porosity.
What is intestinal hyperpermeability?
Intestinal leaky gut syndrome , also known as leaky gut syndrome, is a condition where the protective barrier of our intestines becomes more permeable than normal. The intestine then becomes a veritable "sieve." Normally, the intestinal wall is made up of tightly bound cells, forming a barrier that controls the passage of essential nutrients while preventing unwanted substances from entering our bloodstream. However, in cases of intestinal leaky gut syndrome, this barrier becomes impaired, allowing undigested particles, toxins, and bacteria to pass through the intestinal walls and into the rest of the body via the bloodstream. This situation can lead to an inflammatory response and an imbalance in our immune system , potentially contributing to the development of various health problems.
The importance of a balanced intestinal flora for our overall health
Within our gut lies a vast ecosystem made up of billions of beneficial microorganisms, including good bacteria , known as the gut microbiota . This gut flora plays a crucial role in many aspects of our health: from our immune system to our mood to our digestion. In fact, it acts as a first line of defense against pathogens, promotes nutrient absorption, helps regulate our immune system, and even participates in the production of certain vitamins.
The intestinal wall is permeable to certain compounds because it naturally has pores on its surface, the maximum size of which is determined. This selective permeability allows the passage of certain beneficial molecules and prevents the passage of molecules that would cause harmful consequences if they were to enter our bloodstream. When our intestinal flora is unbalanced, this alters the effectiveness of our intestinal barrier, which can lead to more or less serious health problems.
The main causes of leaky gut
A processed diet, the stress of daily life, medications (antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), intestinal infections (bacterial and fungal), alcohol consumption, nutritional deficiencies... are all causes that can be responsible for intestinal hyperpermeability. As you will have understood, there are many of them and many mechanisms come into play in this process. All these situations lead to a disruption of the balance of the intestinal microbiota, also called intestinal dysbiosis , causing a degradation of the intestinal mucosa. Indeed, the reduction in the proportion of beneficial strains within our intestine, in favor of pathogenic strains, leads to a modulation of the immune response, which contributes to intestinal hyperpermeability. This is a phenomenon to which we are all, more or less, subject. When the intestinal wall is damaged, it becomes permeable to unwanted elements (toxins, germs, allergens, heavy metals, etc.) which can easily enter the body where they should not be. This is when many symptoms can appear.
Symptoms of leaky gut
You may not know this, but the intestinal absorption surface, that is, the surface area of our intestines that allows the absorption of essential nutrients present in our food, is equivalent to the surface area of a tennis court . This is why the breakdown of this barrier, leading to the passage of unwanted substances into the bloodstream, is the starting point for many problems. Intestinal porosity can go unnoticed , as it is difficult to feel it directly. The associated symptoms can also be attributed to other diseases, which makes its diagnosis more complex. However, here is a non-exhaustive list of symptoms frequently associated with intestinal hyperpermeability:
-
Digestive problems: bloating , frequent diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, flatulence, etc.
- Immune system disorders: low resistance to infections and diseases, food allergies and intolerances, autoimmune diseases, etc.
- Chronic fatigue: present even after optimal rest
- Skin problems: acne, eczema, psoriasis, itching…
- Mood disorders: anxiety, mood swings, depression, ADHD…
- Others: recurring headaches, concentration problems, memory loss, irresistible sugar cravings, etc.
How to treat and restore intestinal permeability?
If you experience one or more of the symptoms described above and/or are exposed to factors that promote intestinal hyperpermeability, it is important to consult a doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis. They may prescribe targeted tests (blood/urine tests, etc.). After this, various treatments can be considered to relieve intestinal porosity depending on the identified causes, thus offering a wide range of possible options. Here, we reveal natural solutions to implement in your daily life to combat this phenomenon.
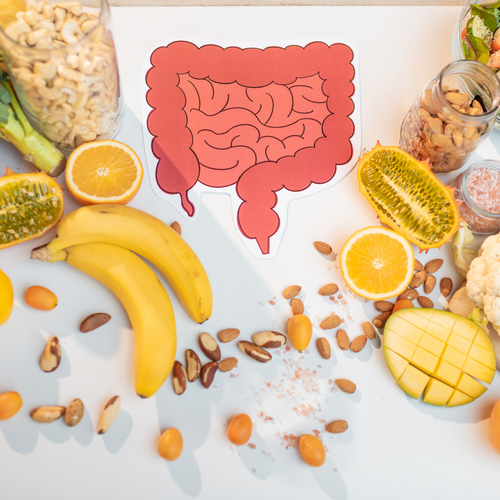
A healthy and balanced diet 🍒
To combat intestinal hyperpermeability, prioritize a healthy and balanced diet. To do this, choose fresh, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, and oilseeds. These foods contain dietary fiber , which is essential for promoting good intestinal health. We also recommend eating foods rich in polyphenols (fruits and vegetables, spices, herbs, and aromatic plants), which relieve inflammation and help treat dysbiosis. Avoid inflammatory foods such as processed (industrial) foods, refined sugars, and saturated fats. Also, make sure you stay hydrated by drinking enough water (at least 1.5 to 2 liters per day). And above all, remember: always listen to your body and adapt your diet according to your individual needs.