What to remember :
- The intestinal microbiota must have a good balance of microorganisms to ensure optimal functions and boost metabolic activity.
- The microbiota is closely linked to the regulation of our weight thanks to the action of the good bacteria that compose it.
- In case of dysbiosis, weight imbalance may occur.
- Diet and lifestyle are essential for taking care of our intestinal microbiota and promoting good regulation of metabolism.
- Providing probiotics and certain herbal and mineral supplements is recommended to aid in weight regulation.
A healthy intestinal microbiota?
The intestinal microbiota represents all the microorganisms present along the digestive tract, particularly the small intestine and colon . Among these microorganisms, we find bacteria, some of which are called probiotics , viruses, fungi and other non-pathogenic organisms. They are essential for promoting good balance in the digestive , immune , metabolic and cerebral systems in particular.
This balance is promoted by a balanced lifestyle, a varied diet adapted to the body's needs, regular physical activity and good stress regulation. However, due to our current lifestyles, this microbiota can be depleted of good bacteria, which creates dysbiosis , a real imbalance of this flora. This can cause an increase in intestinal porosity and intestinal hyperpermeability . In the long term, the assimilation of nutrients is therefore reduced and fatigue and a slowing of the metabolism can occur.
Why take care of your intestinal microbiota?
Taking care of your intestinal microbiota means, above all, protecting the body's primary functions, facilitating proper digestion of food and good production of immune compounds for optimal protection of the body. Indeed, strengthening your microbiota ensures a barrier effect against toxins and pathogenic organisms while facilitating the absorption of nutrients. In addition, by facilitating the action of the immune system, it helps reduce the occurrence of inflammatory pathologies such as diabetes, obesity and many others.
Likewise, it supports brain functions, whether cognitive or emotional, thanks to its 200 million neurons and allows good regulation of its physical and mental capacities.
The unsuspected links between microbiota balance and maintaining good weight regulation
Just like the skin-brain connection, there is a real gut-weight axis.
Indeed, taking care of your intestinal microbiota will help regulate numerous functions including those associated with metabolism and hormonal variations.
Metabolic modulations
Thanks to various studies, we now know that modulation of the intestinal microbiota and therefore that certain bacteria, and in particular their genes, can be at the origin of metabolic and functional changes. Indeed, the action of certain bacteria is linked to specific regulations at the level of the organism. An upheaval in their efficiency or their presence would therefore be at the origin of variations in the degradation of certain food molecules such as starch, in the response to stress and in the production of immune and protective compounds.
In addition, it has been shown that real insulin resistance can develop due to an increase in inflammatory processes at the intestinal level. This resistance is the cause of blood sugar disorders , which can lead to an increase in the occurrence of food cravings and thus promote faster sugar storage and weight regulation disorders.
Balanced diet
Diet is essential to ensure a good balance of the microbiota. This is why providing diverse sources of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates will allow a varied intake of molecules necessary for the development of good bacteria and their activity.
In addition, good absorption of nutrients from food, thanks to a complete microbiota and a reinforced intestinal wall , is essential to avoid the occurrence of deficiencies, facilitate the proper functioning of the body and avoid too rapid storage of ingested sugars . Indeed, fibers as well as proteins and lipids make it possible to reduce the speed of absorption of sugar and therefore its storage in the form of adipose tissue.
The contribution of all these nutrients will help promote a certain composition of microbiota and thus present beneficial bacteria for a metabolism boost and good weight regulation such as Lactobacillus gasseri, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Hafnia alvei HA4597.
How to take care of your microbiota for good weight regulation?
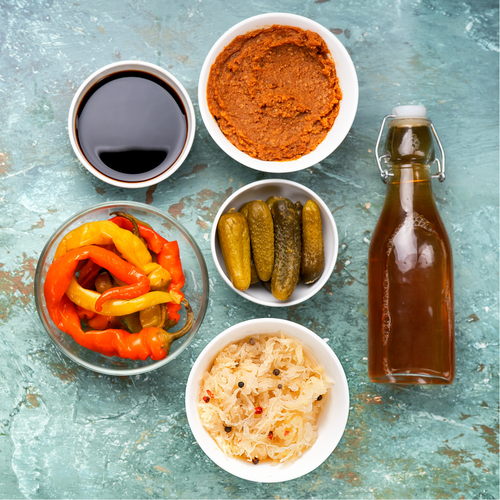
In order to take care of your intestinal microbiota and thus promote good natural weight regulation, it is therefore essential to provide good microorganisms using fermented products such as yogurts, sourdough bread, kefir, and kombucha, kimchi and other lacto-fermented vegetables. Similarly, providing sufficient fiber through diet is essential to nourish these good bacteria. Indeed, also called prebiotics , these fibers found in our fruits and vegetables, cereals, legumes, oilseeds and others are necessary to ensure the proper development of these probiotic bacteria and promote a good balance of the microbiota.
Apart from diet, regular physical activity is strongly recommended. Therefore, it is recommended to walk, climb stairs and engage in manual, leisure or sporting activities .
Finally, taking care of yourmental health is fundamental to ensuring good physiological regulation and avoiding altering the balance of the intestinal flora due to an accumulation of stress molecules.
Sources :
[1] Koutoukidis DA, Jebb SA, Zimmerman M, Otunla A, Henry JA, Ferrey A, Schofield E, Kinton J, Aveyard P, Marchesi JR. The association of weight loss with changes in the gut microbiota diversity, composition, and intestinal permeability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2020068. doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.2020068. PMID: 35040746; PMCID: PMC8796717.
[2] Koutoukidis DA, Jebb SA, Zimmerman M, Otunla A, Henry JA, Ferrey A, Schofield E, Kinton J, Aveyard P, Marchesi JR. The association of weight loss with changes in the gut microbiota diversity, composition, and intestinal permeability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2020068. doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.2020068. PMID: 35040746; PMCID: PMC8796717.
[3] Jian, C., Silvestre, MP, Middleton, D. et al. Gut microbiota predicts body fat change following a low-energy diet: a PREVIEW intervention study. Genome Med 14, 54 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-022-01053-7
[4] Bliesner A, Eccles-Smith J, Bates C, Hayes O, Ho JY, Martins C, Truby H, Nitert MD. Impact of Food-Based Weight Loss Interventions on Gut Microbiome in Individuals with Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2022 May 6;14(9):1953. doi:10.3390/nu14091953. PMID: 35565919; PMCID: PMC9099876.